Foam insulation has become a popular choice for homeowners and builders alike, thanks to its remarkable energy efficiency and versatility. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your loft or walls, understanding how to properly install foam insulation can lead to significant benefits in terms of thermal performance and comfort. In today’s evolving world of building practices, having a solid grasp of foam insulation techniques is crucial for maximizing energy savings. This article will delve into the process, from choosing the right materials to ensuring proper installation, all while keeping you informed about the latest trends and techniques in the insulation industry.
In Brief:
- Understand the types of foam insulation: EPS, XPS, and Polyiso.
- Learn about effective installation methods to enhance thermal barriers.
- Discover air sealing techniques to optimize energy efficiency.
- Explore recommended applications for various building scenarios.
- Identify safe practices and tools needed for effective installation.
Selecting the Right Foam Insulation Materials for Walls and Lofts
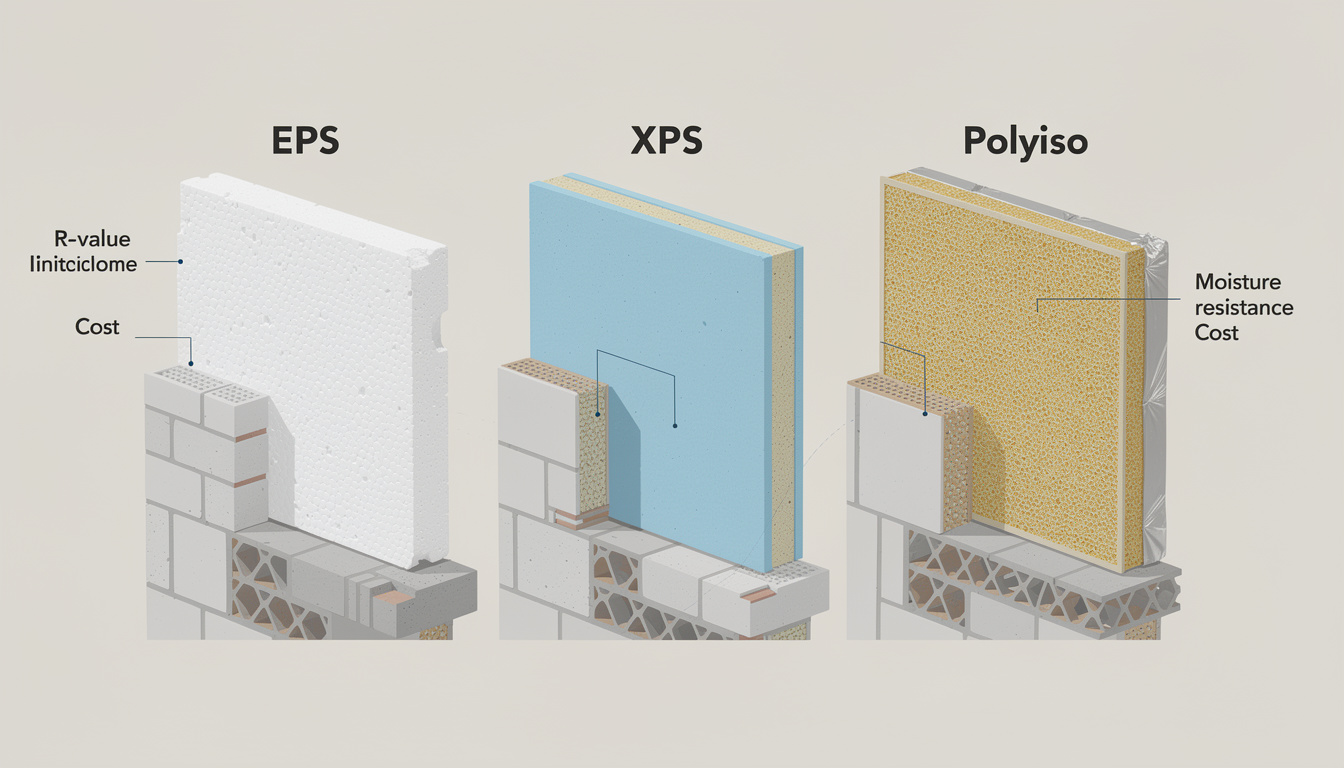
When venturing into foam insulation installation, it’s vital to understand the differences among various materials. Foam board insulation comes in several forms, the primary types being Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Extruded Polystyrene (XPS), and Polyisocyanurate (Polyiso). Each of these options has unique characteristics that suit different needs.
Understanding EPS, XPS, and Polyiso
EPS is the most cost-effective option available. It’s lightweight and features a beaded structure, which makes it familiar to anyone who’s handled standard foam packaging. While its R-value typically ranges from R-3.6 to R-4.2, it performs adequately in colder conditions, making it suitable for below-grade applications.
XPS, identifiable by its signature blue or pink color, offers a higher R-value, generally around R-4.5 to R-5.0 per inch. Its closed-cell structure provides superior moisture resistance compared to EPS, making it ideal for areas prone to dampness. This makes XPS a better choice for exterior wall sheathing where water exposure is a concern.
For the highest performance, Polyiso stands out with an impressive R-value of R-6.0 to R-6.5 per inch, often featuring laminated foil facers. While Polyiso offers the greatest efficiency for above-grade applications, be cautious of thermal drift that can occur at temperatures below 40°F, affecting its R-value.
Choosing the right material involves weighing factors such as cost, R-value requirements, and exposure to moisture. For example, if you reside in a humid environment, XPS might be worth considering due to its moisture-resistant properties. On the other hand, Polyiso is recommended for climates primarily above freezing, where maximizing thermal resistance without increasing thickness is essential.
Installation Techniques for Foam Board Insulation
Now that you’ve made an informed choice about the type of foam insulation, it’s time to tackle the installation process. Starting with the preparation stage is key to a successful insulation project. Proper preparation helps ensure a tight fit and effective performance of the insulation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Install Foam Insulation in Walls
- Measure the Area: Begin by accurately measuring the walls or loft space where you’ll be installing the foam. Accurate measurements help you determine how much material you will need.
- Cutting the Panels: Using a sharp utility knife, cut the foam insulation panels to fit the specific dimensions of your walls. Score the foam deeply and snap it along the line for clean edges.
- Surface Preparation: Before applying the insulation, clean the surfaces thoroughly to create a smooth base. This will help the insulation adhere better.
- Secure the Panels: Depending on the application, you can use specialized adhesives or mechanical fasteners to secure the panels. For walls, cap nails or screws are effective with exterior applications.
- Sealing the Edges: Ensure that all seams, corners, and penetrations are sealed using appropriate flashing tape or foam sealant. This crucial step prevents air leaks.
Each of these steps is critical for ensuring that your foam insulation performs optimally. One common challenge faced during installation is achieving airtight sealing, which limits air movement and enhances energy efficiency. Remember, even the best foam insulation will falter if not installed properly!
Enhancing Energy Efficiency: Air Sealing and Thermal Barriers
One of the remarkable attributes of foam insulation is its ability to act as both a thermal barrier and an air sealing layer. However, leveraging these capabilities requires precision in installation.
The Importance of Air Sealing
Air movement is a leading contributor to energy loss in homes. Foam insulation not only provides a thermally resistant barrier but also keeps unwanted air outside. This prevents heat loss during winter months while keeping your home cool in the summer. To maximize this benefit, every seam needs attention — think of this as creating a fortress against uncontrolled air flow.
A notable tip is to consider including a comprehensive air barrier along with your foam installation. This could mean using sheathing materials on the exterior or applying house wrap underneath the foam boards. A fully sealed assembly transforms a standard insulated wall into a high-performance system that retains energy better.
Benefits of Polyiso and XPS for Building Thermal Barriers
Among rigid foam materials, Polyiso and XPS excel as thermal barriers. Both have closed-cell structures, preventing moisture accumulation that weakens insulating power. This increases long-term effectiveness and durability of your insulation system.
| Material | Typical R-Value (per inch) | Moisture Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| EPS | R-3.6 to R-4.2 | Moderate |
| XPS | R-4.5 to R-5.0 | High |
| Polyiso | R-6.0 to R-6.5 | Very High |
With a careful selection of materials and a keen focus on air sealing, you can elevate your home’s energy efficiency and comfort levels significantly. 🏡
Best Applications and Practices for Insulating Walls and Lofts
Understanding the best applications for foam insulation will allow you to take full advantage of its properties. Whether you’re insulating walls for a new build or retrofitting existing structures, several factors come into play.
Recommended Applications
- 🏢 New Construction: Using foam board as exterior wall sheathing offers a solid, continuous layer of insulation, breaking thermal bridges effectively.
- 🏠 Renovations: When updating existing buildings, adding foam insulation can improve thermal performance significantly.
- 🌧️ Basement Insulation: XPS or EPS is often used to insulate basement walls, preventing moisture intrusion and maintaining comfortable temperatures.
- 🏡 Attics / Lofts: Polystyrene panels can create effective thermal barriers in loft spaces, keeping heat where it needs to be.
In all these scenarios, ensuring a proper fit and providing ongoing maintenance can extend the life of your insulation solution. Staying vigilant about detecting moisture and addressing any issues will preserve the integrity of your insulation system.
Tools and Safety Practices for Installation
When you embark on your foam insulation project, having the right tools is vital. Essential tools include: measuring tape, utility knife, straight edge, and construction adhesive. Safety gear, such as goggles and a dust mask, should be worn during installation to protect against fine particles generated during cutting.
Moreover, always remember that many building codes require fire-rated thermal barriers for foam insulation installed indoors. A layer of drywall should be applied over the insulation to prevent fire hazards. Following these guidelines ensures that your project is not only effective but also safe.
Can I install foam insulation in finished walls?
Yes, you can add spray foam insulation to finished walls by drilling small access holes and filling the cavities with foam, without removing the drywall.
What are the safety standards for foam insulation installation?
Always cover foam insulation with a fire-rated thermal barrier, like drywall, as required by local building codes.
How does thermal drift affect Polyiso insulation?
Thermal drift can temporarily decrease the R-value of Polyiso in very cold temperatures, making it less efficient. Ensure this is taken into account during material selection.
What are some common mistakes when installing foam board insulation?
Common errors include improper sealing of seams, incorrect material choice, and neglecting to use a fire-rated barrier for indoor installations.
How important is the air sealing process when installing insulation?
Air sealing is crucial for maximizing energy efficiency and ensuring that the insulation performs as intended, preventing heat loss.



