Insulation plays a vital role in maintaining the comfort and energy efficiency of our living and working spaces. Understanding the differences between open-cell and closed-cell foam insulation can make a significant impact when it comes to selecting the right material for various applications. Whether you are renovating your home or working on a new construction project, knowing the unique characteristics and advantages of these two types of foam can guide your decision-making process. From their structural properties to their performance metrics, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of how open-cell and closed-cell foam insulation differ and how to choose the best option for your needs.
In brief:
- 🔹 Open-Cell Foam: Lightweight, flexible, great for soundproofing, lower R-value.
- 🔹 Closed-Cell Foam: Denser, water-resistant, better insulation, higher R-value.
- 🔹 R-Value: Measures thermal resistance; closed-cell offers higher ratings.
- 🔹 Use Cases: Open-cell for interior spaces; closed-cell ideal for damp or outdoor environments.
- 🔹 Cost Consideration: Open-cell is more budget-friendly; closed-cell is a long-term investment.
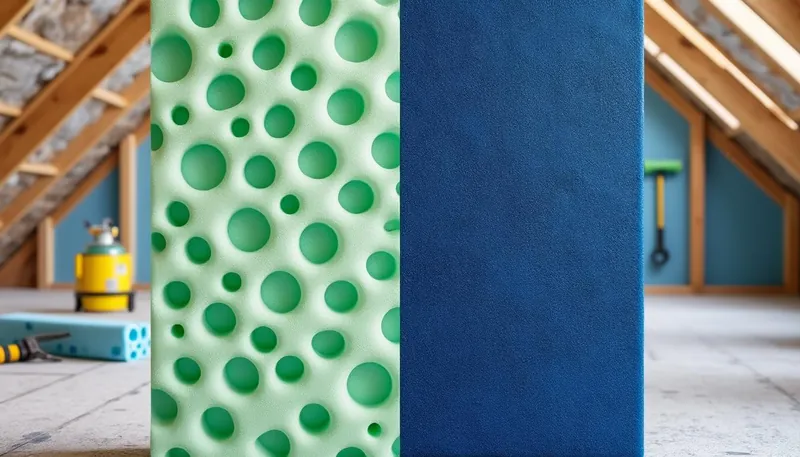
Understanding Open-Cell Foam Insulation
Open-cell foam is a lightweight and flexible insulation material crafted with interconnected pockets that allow air to circulate freely. This design gives it a sponge-like texture, making it excellent for filling awkward spaces like attics and corners. For many applications, open-cell foam serves as an ideal choice for those looking for a material that can both insulate and muffle sound.
Characteristics of Open-Cell Foam
One of the most notable features of open-cell foam is its ability to expand significantly after application, enabling it to fill gaps easily. This property is especially valuable when insulating hard-to-reach areas in retrofitting projects. An important point to consider is its lower R-value, which generally ranges from 3.5 to 4 per inch. While this makes it less effective in extreme climates, it is often sufficient for indoor applications where temperature control isn’t a huge concern.
Furthermore, open-cell foam is less expensive than its closed-cell counterpart, often making it a go-to option for budget-conscious projects. However, its porous structure results in moisture absorption, which may limit its functionality in humid or damp environments. Because of this, open-cell foam is rarely recommended for outdoor applications or areas prone to wetness.
| Feature | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|
| Density | ~0.5 pounds per cubic foot |
| R-Value | 3.5 – 4 per inch |
| Water Resistance | Poor |
| Sound Absorption | Good |
| Application Suitability | Indoor Use |

When to Use Open-Cell Foam
This type of foam is particularly suitable for applications requiring soundproofing. For instance, if you’re constructing a music studio or a home theater, open-cell foam excels in sound absorption due to its structure. In addition, it performs well in interior wall cavities, where minimizing the flow of sound between rooms is important.
Open-cell foam insulation is also valuable for HVAC applications, especially around ducts where flexibility is desired. Despite its limitations in moisture resistance, with appropriate installation techniques and protective barriers, it can work effectively in controlled environments.
Diving into Closed-Cell Foam Insulation
On the other side of the spectrum, closed-cell foam is known for its denser, more rigid characteristics. Closed-cell foam consists of cells that are fully encapsulated, meaning that air and moisture cannot permeate the material. The tighter structure gives closed-cell foam a range of benefits, particularly in terms of thermal resistance and moisture control.
Characteristics of Closed-Cell Foam
This type of foam boasts a higher R-value, typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, making it a superior choice for insulation, especially in extreme climates. Closed-cell foam is ideal for locations where moisture may be an issue, such as basements and areas exposed to high humidity. Its water-resistant properties prevent the growth of mold and also contribute to the longevity of the insulated structure.
Closed-cell foam can also preserve structural integrity thanks to its rigidity, which can contribute to the strength of walls when applied correctly. The cost factor is higher compared to open-cell foam, but the long-term energy savings and durability often justify the investment.
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam |
|---|---|
| Density | ~1.75 pounds per cubic foot or more |
| R-Value | 6 – 7 per inch |
| Water Resistance | Excellent |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate |
| Application Suitability | Outdoor Use |

Advantages and Applications of Closed-Cell Foam
Given its robust properties, closed-cell foam is ideal for various applications where water damage is a concern. For instance, it can be employed in exterior walls, roofs, and basement foundations. Brands like Demilec, Icynene, Johns Manville, and Owens Corning offer advanced closed-cell foam solutions that enhance building energy efficiency.
Moreover, closed-cell foam acts as a vapor barrier, reducing the likelihood of moisture build-up inside structures. This characteristic is crucial for preventing mold growth and ensuring a healthier indoor environment. Closed-cell foam also expands about an inch when sprayed, enabling it to achieve high R-values in fewer applications.
R-Value Differences: A Comprehensive Look
The R-value is a critical metric in determining the effectiveness of insulation materials. It indicates how well a material resists heat flow; the higher the R-value, the better the insulation performance. Thus, understanding the R-value differences between open-cell and closed-cell foam will help in making informed choices depending on climate and building requirements.
Comparative R-Values and Implications
As noted earlier, open-cell foam has an R-value ranging from 3.5 to 4, making it less effective for insulation in cold climates. In comparison, closed-cell foam provides an R-value between 6 to 7, making it optimal for various settings, particularly for residential and commercial structures exposed to elements.
| Type of Foam | R-Value per Inch | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Cell Foam | 3.5 – 4 | Interior Walls, Soundproofing |
| Closed-Cell Foam | 6 – 7 | Basements, Exterior Walls, Roofs |
Ultimately, the choice between open-cell and closed-cell foam boils down to cost, application, and desired outcomes from the insulation. Those looking for a budget-friendly solution with soundproofing capabilities may lean toward open-cell options.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Project
Selecting the right insulation requires a careful assessment of specific needs and the environmental context. To simplify the decision-making process, here’s a breakdown of factors to weigh when choosing between open-cell and closed-cell foam. Consulting with professionals like BASF, CertainTeed, Touch ‘n Foam, Tiger Foam, Foam It Green, and Lapolla can provide valuable insights based on current standards and practices.
Key Considerations for Selecting Insulation
- 🔍 Environment: Consider the climate and specific moisture conditions of the application area.
- 💰 Budget: Weigh the cost of open-cell versus closed-cell foam in relation to long-term benefits.
- 🔊 Sound Requirements: Determine whether soundproofing is a priority for your project.
- 🔒 Durability: Look for materials that can withstand environmental factors, especially in outdoor applications.
- 🏗️ Structural Needs: Assess whether added rigidity is necessary for wall integrity and insulation performance.
Choosing between open-cell and closed-cell foam insulation can be a nuanced process. Assess your project environment, long-term goals, and have discussions with insulation experts to ensure you make the best choice.
What are the applications of open-cell foam?
Open-cell foam is commonly used in indoor spaces for soundproofing, HVAC applications, and areas where flexibility is required.
Is closed-cell foam better for insulation?
Yes, closed-cell foam generally provides higher R-values and is water-resistant, making it suitable for outdoor and damp environments.
What brands offer quality foam insulation?
Prominent brands include Demilec, Icynene, Johns Manville, Owens Corning, BASF, CertainTeed, Touch ‘n Foam, Tiger Foam, Foam It Green, and Lapolla.
How does the R-value impact insulation performance?
The R-value indicates how well a material resists heat flow; a higher R-value means better insulation effectiveness.
Can I use open-cell foam in a humid environment?
It’s not recommended, as open-cell foam tends to absorb moisture, potentially leading to mold and deterioration.